Molecular Biology
2.1 Molecules to Metabolism
Molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved.
Molecular biology = branch focused on structures and functions at a molecular level.
- The science of molecular biology aims to explain living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved.
Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist.
Atom = a single particle of an element, consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
Molecule = a group of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds.
Organic compound = consists of carbon and is found in living things.
- Exceptions: carbides, carbonates, oxides of carbon, cyanides.
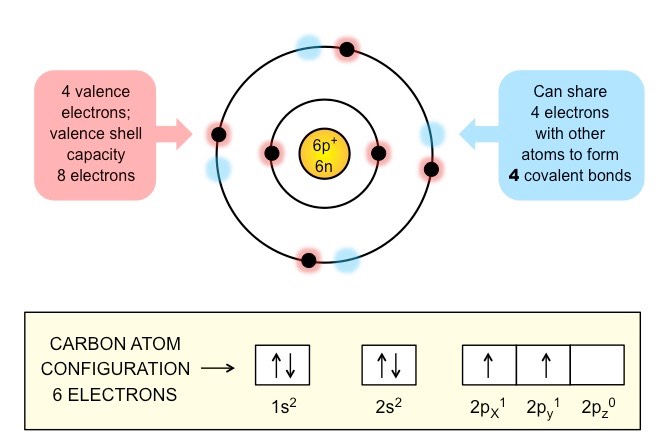
Forms diversity by:
- Forming four covalent bonds, hence being the backbone for molecules.
- Forming chains.
- Ring structures.
- Linking together.
- Forming double bonds with itself.
- Bonding with either one atom or multiple ones.
Life is based on carbon compounds including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrate = organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, with a ratio of two hydrogens to one oxygen.
- Primary function: source of energy.
- Secondary function: short-term energy storage.
- Other functions: works as recognition molecule, structural component in DNA and RNA.
Lipids = class of non-polar, hydrophobic molecules that are insoluble in water, and may come in a variety of forms, namely simple, complex or derived.
- Primary function: major component of cell membranes in phospholipids and cholesterol.
- Secondary function: long-term energy storage.
- Other functions: can be used as a signalling molecule.
Proteins = large, complex molecules, composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
- Primary function: regulatory molecules used in catalysis.
- Secondary function: may function as a structural molecule.
- Other functions: play a role in cellular signalling.
Nucleic Acids = chains of subunits called nucleotides, which contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus, and are found in the form of either ribonucleic acid (RNA), or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
- DNA = stores genetic information, replicates genetic data during cell division and provides scope for mutation.
- RNA = performs the work of certain enzymes, forms a transcription base and helps in translation.
Metabolism is the web of all the enzyme-catalysed reactions in a cell or organism.
Metabolism = integrated network of all the biochemical reactions of life.
1563449167.png)
Functions of metabolic pathways:
- Providing a source of energy for cellular processes.
- Enabling the synthesis and assimilation of new materials for use in the cell.
Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions.
Anabolism = the building up of complex molecules from smaller ones.
Condensation reaction = formation of larger molecules involving the removal of water from smaller component molecules.
- Uses energy to construct new bonds, hence is called endergonic.
- Usually involves reduction reactions.
- Example: gluconeogenesis.
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers.
Catabolism = the breaking down of complex molecules in the biochemistry of cells.
View count: 4808